- supplying personal protective equipment (PPE),
- providing quantitative respirator fit testing,
- providing respirator medical evaluations,
- our monthly Safety Suzy newsletter with content on asbestos, mold, indoor air quality, and occupational safety and health information,
- our blog where we post items of interest and discussion,
- our negative air app,
- our air sampling charts,
- our training library,
- our partnership with SiteDocs,
- and all of it found on FEDTC's website.
Future Environment Designs Training Center specializes in asbestos, indoor air quality, industrial hygiene, and occupational safety training programs. We offer New York State asbestos and mold certification courses. We design, develop, and maintain the various indoor air quality, asbestos, and safety programs that are Keeping Your Employees Safe.
Search This Blog
Friday, October 10, 2025
Future Environment Designs, Inc. Celebrates 37 Years in Business With a New Program Called "After The Refresher"
Tuesday, February 18, 2025
The Role of Asbestos Inspections in Construction Safety: Don't Miss the Asbestos Inspection Panel at PACNY's Environmental Conference!
In the construction world, one of the most pressing concerns for worker safety is the potential asbestos exposure. This hazardous material, once commonly used in various building materials for its fire-resistant and other properties, has been linked to serious health risks, including lung cancer, asbestosis, and mesothelioma. Asbestos exposure remains a significant threat, especially in older buildings undergoing renovation or demolition. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) have set strict guidelines to minimize this danger, but compliance hinges on one key factor: thorough and accurate asbestos inspections.
To explore the intricacies of asbestos inspections, Angelo Garcia, III of Future Environment Designs, Inc., will be moderating a distinguished panel at PACNY's 2025 Environmental Conference on Thursday, February 27, 2025. The panel will dive deep into the importance and differences in asbestos inspections from various perspectives. This includes Tom Laubenthal of TGL Consulting and ASTM E2356 Chairman, who will discuss the ASTM asbestos inspection standard, Chris Alonge now with Dormitory Authority of the State of New York (DASNY) who will provide insights from an owner's perspective, Marc Rutstein from Environmental Consulting & Management Services, who will offer a consultant's viewpoint and highlight the differences between NYCDEP and NYSDOL inspections, and Matt Brooks from International Asbestos Removal (IAR), who will speak on the contractor’s perspective.
 |
| Asbestos pipe insulation with fitting insulation |
Asbestos inspections play a vital role in identifying materials that may contain asbestos before they are disturbed. This proactive approach not only prevents worker exposure but also ensures that proper abatement procedures are followed. A well-executed asbestos inspection is the first line of defense against the release of airborne asbestos fibers, which can be deadly when inhaled.
Understanding the Importance of Homogeneous Areas
At the heart of every asbestos inspection is the process of determining whether a material is classified as a surfacing material, thermal system insulation, or miscellaneous material. Once the material type is identified, the inspector must establish whether the materials are homogeneous. According to the EPA’s Asbestos Hazard Emergency Response Act (AHERA), a homogeneous area is defined as one where the material is uniform in color and texture.
 |
| Floor tiles and numerous homogeneous areas |
However, that is not the only definition of homogeneous area/material. For example, the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has established a Standard Practice for Comprehensive Asbestos Surveys (ASTM E2356-18) in this standard the definition of homogeneous area is surfacing material, thermal system insulation material, or miscellaneous material that is uniform in color and texture and apparent or known date of installation. The other definitions that are used by inspectors also include some reference to installation or formulation in addition to color and texture. This classification is crucial because it informs the number of samples that must be taken to accurately assess the presence of asbestos.
Sampling Procedures: The Foundation of a Successful Inspection
For surfacing materials, the size of the homogeneous area directly influences the number of samples needed. Under the EPA’s guidelines, inspectors follow the “3-5-7 rule.” This means that three samples are required for areas smaller than 1,000 square feet, five samples for areas between 1,000 and 5,000 square feet, and seven samples for areas larger than 5,000 square feet. Additionally, the EPA’s “Pink Book,” formally known as Asbestos in Buildings: Simplified Sampling Scheme for Friable Surfacing Materials, recommends taking nine samples per homogeneous area, regardless of the square footage, for increased accuracy.
 |
| Asbestos Fireproofing |
For thermal system insulation, the process differs slightly. Inspectors must determine if the material is homogeneous, patch material, or material used on fittings like elbows and valves. Homogeneous areas of thermal system insulation require three samples, while patch materials smaller than six linear or square feet only need one sample (the only time one sample is allowed). Cement or plaster used on fittings must be sampled based on the specific mechanical system in question, and a minimum of two samples is required for each system. However, the EPA in A Guide to Performing Reinspections Under AHERA strongly advises taking at least three samples in larger homogeneous areas, even if regulations don't mandate it.
For materials such as joint compound and add-on materials, however, the EPA’s “Asbestos Sampling Bulletin dated September 30, 1994” specifies that three samples are required for each material. These distinctions are critical for asbestos inspectors to ensure compliance and accuracy in their assessments (see our original blog post on asbestos surveys).
In May 2007, the EPA provided important clarification on sampling requirements. Mr. Chris Alonge, at the time, was working for New York State Department of Labor (NYSDOL) and he requested clarification regarding the number of samples that should be taken for each suspect asbestos-containing homogeneous miscellaneous material. The clarification was distributed by the Professional Abatement Contractors of New York (PACNY) in November 2007. According to this clarification, the minimum number of samples that should be taken of miscellaneous materials (i.e., floor tiles, roofing, caulk, ceiling tiles) is two (see our original blog post on this issue).
 |
| Respirator and protective clothing should be worn by the inspector during sampling |
Following proper sampling protocols is crucial because asbestos is considered present if any one of the samples from a homogeneous area contains more than 1% asbestos. Conversely, if all samples return asbestos concentrations at or below 1%, the area is deemed asbestos-free—though it’s important to remember that materials containing 1% or less of asbestos are still regulated under OSHA’s asbestos standard (see the Varga letter).
The Legal and Health Implications of Incomplete Inspections
Inadequate or incorrect asbestos inspections can have severe consequences. From a legal standpoint, failing to adhere to EPA and OSHA regulations can result in hefty fines and penalties. Remember neither regulation has a specific end date for buildings not containing asbestos (see our post Is There an Appropriate End Date for Asbestos Use?). More importantly, from a health perspective, improperly identifying or failing to identify asbestos-containing materials (ACMs) can expose construction workers to dangerous fibers, leading to long-term health problems. Given that asbestos-related diseases may take decades to develop, the human cost of negligent inspections can be devastating.
 |
| The closet door with asbestos core was cut without any precautions costing over $30,000 to clean up the contamination. |
Mr. Tom Laubenthal wrote EPA in November 2014 regarding The Standard Practice for Comprehensive Asbestos Surveys (ASTM E2356-18) Pre-Construction Survey (section 8 of the standard) meeting the requirement under National Emissions Standards of Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAPS) of a thorough inspection. EPA responded that they would expect an owner/operator to follow the steps in Sections 1 through 5 and Section 8 to comply with the NESHAPS regulation. This standard provides a framework for conducting thorough asbestos inspections, particularly in pre-construction scenarios, ensuring that no asbestos-containing material goes unnoticed.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Inspections
Asbestos inspections are the cornerstone of any effort to protect workers from exposure to this hazardous material. By adhering to the EPA’s and OSHA’s strict sampling and inspection guidelines, inspectors can identify asbestos-containing materials before they are disturbed, reducing the risk of airborne fibers and subsequent health issues. Given the serious implications of asbestos exposure, thorough inspections are not just a regulatory requirement—they are a moral imperative in safeguarding the health and well-being of workers.
 |
| Asbestos Floor Tiles disturbed before identification led to a clean-up costing over $250,000 |
In the end, the responsibility lies with all stakeholders—building owners, contractors, and asbestos inspectors alike—to ensure that every construction or renovation project is free from asbestos hazards. As inspectors, staying current on regulations, maintaining rigorous sampling standards, and educating clients on the risks and regulations associated with asbestos are critical components in this ongoing battle against a deadly substance.
The asbestos inspection panel promises to be an invaluable session for professionals across the construction, consulting, and regulatory industries. With these diverse viewpoints, we aim to shed light on the critical role inspections play in protecting workers and ensuring compliance with ever-evolving asbestos regulations. Asbestos inspections are not just about checking boxes—they are about saving lives.
Monday, April 08, 2024
Chrysotile Asbestos Banned? More Like Certain Conditions of Use Will Be Eventually Banned!
 |
| Chrysotile Asbestos |
The final rule can be found on EPA's website here. The document consists of 40 pages (pages 21970 to 22010). However, the rule is found on page 22005 (35 pages after the beginning of the document, meaning the rule consists of only 5 pages). Subpart F - Chrysotile Asbestos starts with the different Sections of the Rule:
- 751.501 General
- 751.503 Definitions
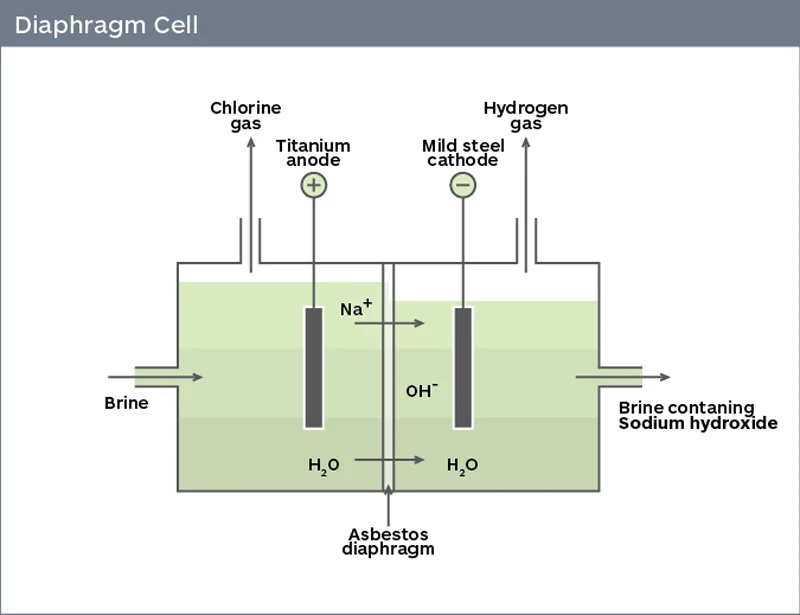
- 751.505 Manufacturing, processing and commercial use of chrysotile asbestos diaphragms in the chlor-alkali industry.
- 751.507 Certification of compliance for the chlor-alkali industry.
- 751.509 Other prohibitions and restrictions of the manufacturing, processing and commercial use of chrysotile asbestos.
- 751.511 Interim workplace controls of asbestos exposures.
- 751.513 Disposal.
- 751.515 Recordkeeping.
- Section (a) states, after May 28, 2024, all persons are prohibited from manufacture (including import) of chrysotile asbestos, including any chrysotile asbestos-containing products or articles, for diaphragms in the chlor-alkali industry.
- Section (b) states, after May 28, 2029, all persons are prohibited from processing, distribution in commerce, and commercial use of chrysotile asbestos, including any chrysotile asbestos-containing products or articles, for diaphragms in the chlor- alkali industry, except as provided in paragraphs (c) through (d) of this section.
- Section (c) Any person who meets all of the criteria of this paragraph (c) may process, distribute in commerce and commercially use chrysotile asbestos, including any chrysotile asbestos- containing products or articles, for diaphragms in the chlor-alkali industry at no more than two facilities until May 25, 2032: (1) On May 28, 2024, the person owns or operates more than one facility that uses chrysotile asbestos in chlor-alkali production; (2) The person is converting more than one facility that the person owns or operates that as of May 28, 2024 uses chrysotile asbestos in chlor-alkali production from the use of chrysotile asbestos diaphragms to non-chrysotile asbestos membrane technology, and by May 28, 2029, the person has ceased all processing, distribution in commerce and commercial use of chrysotile asbestos at one (or more) facility undergoing or that has undergone conversion to non-chrysotile asbestos membrane technology; and (3) The person certifies to EPA compliance with the provisions of this paragraph, in accordance with §751.507.
- (d) Any person who meets all of the criteria of this paragraph (d) may process, distribute in commerce and commercially use chrysotile asbestos, including any chrysotile asbestos- containing products or articles, for diaphragms in the chlor-alkali industry at not more than one facility until May 26, 2036: (1) On May 28, 2024, the person owns or operates more than two facilities that use chrysotile asbestos in chlor-alkali production; and (2) The person is converting more than two facilities that the person owns or operates that as of May 28, 2024 use chrysotile asbestos in chlor-alkali production from the use of chrysotile asbestos diaphragms to non-chrysotile asbestos membrane technology: (i) By May 28, 2029, the person has ceased all processing, distribution in commerce and commercial use of chrysotile asbestos at one (or more) facility undergoing or that has undergone such conversion; and (ii) By May 25, 2032 the person has ceased all processing, distribution in commerce and commercial use of chrysotile asbestos at two (or more) facilities undergoing or that have undergone conversion to non-chrysotile asbestos membrane technology; and (3) The person certifies to EPA compliance with the provisions of this paragraph, in accordance with §751.507.
- Prohibit the manufacture (including import), processing, use, distribution in commerce and commercial use of chrysotile asbestos, including any chrysotile asbestos-containing products or articles, for sheet gaskets in chemical production and require interim workplace controls for certain commercial uses after May 27, 2026. With exceptions for titanium dioxide production until May 28, 2029, and processing nuclear material at the Savannah River Site until December 31, 2037.
- Prohibit the manufacture (including import), processing, distribution in commerce, and commercial use of chrysotile asbestos, including any chrysotile asbestos-containing products or articles, for oilfield brake blocks, aftermarket automotive brakes, and linings, other vehicle friction products, and other gaskets after November 25, 2024;
- Prohibit the manufacture (including import), processing, and distribution in commerce of chrysotile asbestos, including any chrysotile asbestos-containing products or articles, for consumer use of aftermarket automotive brakes and linings and other gaskets after November 25, 2024.
- All of these have exceptions to the distribution in commerce prohibition if they are already installed.
 |
| https://www.asbestos.com/occupations/auto-mechanics/ |
- Beginning November 5, 2024,....no person is exposed to an airborne concentration of chrysotile asbestos in excess...0.005 fibers per cubic centimeter (f/cc) as an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA). Remember the OSHA Permissible Exposure Limit for asbestos is 0.1 f/cc as an 8-hour time weighted average. The ECEL is a 20 times reduction from the PEL.
- Requires initial (performed as of May 28, 2024, and no later than November 25, 2024) & periodic exposure monitoring (performed within three months or six months based on previous results).
- Method of Monitoring utilizes OSHA 1910.1001 Appendix A, OSHA method ID-160, or the National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) 7400 method. Allowance for the NIOSH 7402 method to adjust the analytical result to include only chrysotile asbestos.
 |
| Personal Sampling Pump |
- If exposure monitoring indicates the exposure is above 0.00view 5 f/cc and less than or equal to 0.05 f/cc. The employer must provide either a half-mask supplied air (SAR) or airline respirator operated in demand mode or a half-mask self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) respirator operated in demand mode.
- If exposure monitoring indicates the exposure is above 0.05 f/cc and less than or equal to 0.125 f/cc. The employer must provide a loose-fitting facepiece supplied air (SAR) or airline respirator operated in continuous flow mode.
 |
| Supplied airline respirator |
"Respirators which use filters to remove contaminants from the air do not provide as high a degree of protection for workers as respirators which supply clean pressurized air to the workers from a protected source."
- The National Law Review - EPA Bans Ongoing Uses of Asbestos https://www.natlawreview.com/article/epa-bans-ongoing-uses-asbestos
- ADAO's FAQs and Quotes on EPA Part 1 Chrysotile Asbestos Rule
https://www.asbestosdiseaseawareness.org/newsroom/blogs/faqs-and-quotes-on-epa-part-1-chrysotile-asbestos-rule/
Monday, October 24, 2022
The Reality of Asbestos Clearance Air Sampling! Are You Sampling Enough?
We attended the Environmental Information Association (EIA) 2022 National Conference and Exhibition in Phoenix, Arizona from March 20, through March 23, 2022. We attended several sessions regarding asbestos where we discussed with some attendees asbestos clearance air sampling and what are the Federal requirements. Based on those discussions we figured it was time to write an article on this topic. To make sure we wrote this article based on general industry practice, versus what we are used to in New York State and New York City, we consulted with Mr. Tom Laubenthal, of TGL Consulting, Inc., and Mr. Dana Brown, of Time's Dark Captains. Since everything else seems to start with the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA's) Asbestos-Containing Materials in Schools Rule (40 CFR Part 763, Subpart E, known in the industry as the Asbestos Hazard Emergency Response Act (AHERA)) why don't we start there? The AHERA regulation remember applies to schools from Kindergarten to 12th grade (K-12), both public and private schools. The requirements are found in two sections of the rule:
- Response Actions; §763.90 (i)
- Appendix A (to Subpart E) - Interim Transmission Electron Microscopy Analytical Methods - Mandatory and NonMandatory - and Mandatory Section to Determine Completion of Response Actions
For all intents and purposes, these methods serve as the industry standard when final clearance is performed for most asbestos abatement projects, especially when areas are to be re-occupied. We’ll discuss applicability issues as we go.
 |
| TEM Analysis |
First, let's discuss the requirement for aggressive clearance sampling. In the AHERA regulation, aggressive sampling means floors, ceilings, and walls shall be swept with the exhaust of a minimum one (1) horsepower leaf blower. Some states and specifications may also require the use of fans as described in the non-mandatory section of Appendix A. The non-mandatory section states, that stationary fans shall be placed in locations that will not interfere with the air monitoring equipment. Fan air is directed toward the ceiling. One fan shall be used for every 10,000 cubic feet (CF) of a worksite. This is required in the New York State Department of Labor's Asbestos Regulation Industrial Code Rule 56 (NYSDOL ICR56) and the New York City Department of Environmental Protection Asbestos Regulation Title 15 (NYCDEP Title 15). However, NYSDOL ICR56 also requires one fan per room in addition to the one fan per 10,000 CF.
 |
| This is not in the spirit of the AHERA/NYSDOL ICR56/NYCDEP Title 15 requirements for aggressive clearance sampling. Thank you Greg Mance for the photo. |
As defined by the AHERA rules, final clearance air sampling can be done by phase contrast microscopy (PCM) methodology for projects less than or equal to 160 square feet (SF) or 260 linear feet (LF) by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) 7400 methodology (Issue 3: 14 June 2019 is the current issue). For projects greater than 160 SF or 260 LF clearance shall be done by the AHERA transmission electron microscopy (TEM) method (requirements at 763.90 (i) (4) and Appendix A).
 |
| Graphic courtesy Tom Laubenthal |
There are some similarities between the AHERA TEM and NIOSH 7400 methods. For example, the AHERA TEM method (Appendix A) allows for the use of either a 25-millimeter (mm) filter cassette or a 37-mm filter cassette. We haven't used a 37-mm cassette since the industry switched from the old asbestos sampling method NIOSH P&CAM 239 to the NIOSH 7400 method that was formally adopted into AHERA. For sampling, whether it is the AHERA TEM method or the NIOSH 7400 method, we use a 25-mm 3-piece cassette with 50-mm electrically conductive extension cowl cassettes. The two methods require the filter cassette to face 45 degrees downward from the horizontal. The filter material used is mixed cellulose ester (MCE). AHERA TEM method does allow for the use of polycarbonate (PC) filters as well. The PC filters fell out of favor because post-sampling handling was more problematic than the MCE filters. With PC filters, if samples sent to the lab are not handled carefully, the sampled fibers can move significantly from the filter surface. This was widely discussed in the industry in the 1980s. Since then, only MCE filters are used outside of specialty applications.
 |
| The filter cassette is to face 45 degrees downward from the horizontal. |
Both methods require blanks, however, that is where the similarities end. The AHERA TEM method requires three blanks two field blanks and one laboratory (sealed) blank. While the NIOSH 7400 method requires a minimum of two blanks or 10% of samples collected with a maximum of 10 blanks. How the blanks are handled is different as well. The AHERA TEM method laboratory (sealed) blank is not opened and kept sealed, while the field blanks are opened for 30 seconds at the entrance to each abatement area and one at an ambient area. While the NIOSH 7400 method requires the blanks to be opened at the same time as the other cassettes just prior to sampling and stored with the top covers of the cassettes that are running and remain open for the duration of sampling (here is an interesting difference, in some places the cassettes are stored in the box with the lid closed or, the way we were taught, they are placed in a Ziploc bag that is used to deliver the samples to the laboratory).
 |
| A typical box of air sampling cassettes |
Another difference is that with the AHERA TEM method we use a 0.45-micron (µm) MCE filter and the NIOSH 7400 method uses a 0.8 µm MCE filter. This refers to the size of the air passages in the filter material. Filter manufacturers will color code or mark the label so that the type of filter within the cassette assembly is known to the user and the laboratory.
 |
| TEM filter is 0.45-micron. PCM filter is 0.8-micron. |
Let's get to some of the interesting items such as how the samples are taken and how many are required. The AHERA TEM method is straightforward, it requires 5 samples inside the work area and 5 samples outside the work area that represent air entering the abatement site plus the blanks (as mentioned above) for a total of 13 samples. These samples should run from 1 to less than 10 liters per minute (LPM) for a total volume of air greater than 1199 liters or greater (see Table 1 below for the recommended sampling volume range for this method, typically the volume range is between 1200 liters and 1800 liters). It is interesting that the maximum flow rate is less than 10 LPM. It would be interesting to find out how many in the industry actually sample at less than 10 LPM (i.e., 9.9 LPM versus 10 LPM). Likely most of the industry merely samples at 10 LPM. The statistical difference between 10 and 9.9 LPM, some regulators insist upon, is statistically insignificant and will affect method performance in no discernable manner. Either way, this means your clearance samples will take a little over 2 hours to collect.
 |
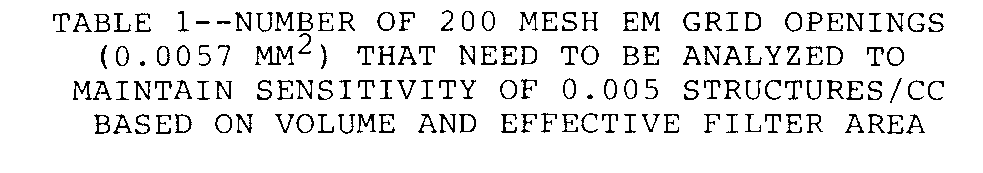 |
In speaking with Mr. Tom Laubenthal, we learned at the time this method was developed it became known through the research involved that flow rates higher than 10 LPM could cause fibers to impact the MCE filters vertically and not horizontally to the filter surface. This makes the sample analysis, counting, and identification, difficult and likely biased. This is also the reason the method specifies a second MCE filter under the 0.45 µm sampling filter and the 5 µm diffuser. This additional filter is placed in this manner to attempt to create an even flow across the filter surface so that fibers impact the filter uniformly. Since the fibers are lying flat on the filter this is the reason for turning the sample upright before interrupting the pump flow to ensure the fibers remain on the filter.
 |
| Sampling Cassette Configuration |
In the AHERA TEM method, the clearance samples pass when the average concentration of the five samples inside the work area does not exceed 70 structures per square millimeter (s/mm2). See AHERA at 763.90 (i) (3) for an optional clearance test based on the z-test which compares the outside and inside air samples. This is rarely necessary. But cases have occurred when contamination can exist in the air outside the work area that could cause a failure in the work area.
 |
| This TEM asbestos image is from the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) "Asbestos Fibers and Other Elongate Mineral Particles: State of the Science and Roadmap for Research" |
The NIOSH 7400 method for final clearance is also interesting when it comes to how the sample is taken and how many are based on the project. For schools, when PCM is allowed, it's 5 samples inside the work area. What's interesting is that the clearance is based on each sample and each sample must be less than or equal to a limit of quantitation (LOQ) for PCM of 0.01 fibers per cubic centimeter (f/cc). Well according to the NIOSH 7400 method how do you achieve clearance at that LOQ? This concept of LOQ is not a concept understood by many that use the NIOSH 7400 method for all its purposes. In the NIOSH 7400 method, this issue is addressed as follows in the section "Sampling", number 4 on page 4. It utilizes the formula below to determine the amount of time needed to achieve the fiber density, E, for optimum filter loading. So, the minimum density the method allows is 100 fibers per square millimeter (mm2). The Ac is the collection area for a 25-mm cassette which is 385 mm2. The Q is the sampling flow rate in LPM, so let's say that is 16 (the maximum flow rate allowed by the method). The L is the concentration of fibers in the air, we are looking to achieve clearance at 0.01 fibers/cubic centimeters (f/cc). So if you plug these numbers into the formula you get a time of 240.6 minutes, which means the sample would have to run for a little over 4 hours at 16 liters per minute (total volume of air of 3,850 liters).
Realize that is running the sample at 16 LPM. If your pump/flowmeter can only go to 15 LPM then you would have to run the sample for 256.7 minutes which is just short of 4 hours and 15 minutes. The lower the flow rate, the longer time it will take to meet sample volume requirements.
 |
| Airbox High-Performance Air Sampler |
Many believe or have been misled to believe that PCM sampling is the same as TEM sampling in terms of sampling volume. This is not the case. A PCM sample volume meeting AHERA clearance requirements are not at 1200 liters. To do so is outside of the NIOSH 7400 method requirements for this purpose. In the NIOSH 7400 method, the issue regarding "relatively clean" environments" is addressed on page 4, number 4, note number 1 which states "In relatively clean atmospheres, where targeted fiber concentrations are much less than 0.1 f/cc, use larger sample volumes (3000 to 10,000 liters) to achieve quantifiable loadings." Even though the formula calculates that 3,850 liters of air should be collected, many people use note 1 to collect 3,000 liters of air for clearance. Either way clearance samples should be collected using no less than 3,000 liters of air as the minimum allowed for the NIOSH 7400 method requirements and AHERA compliance.
 |
| PCM image of fibers |
The true problem is the NIOSH 7400 was never designed as a clearance tool, it was designed as a personal air sampling method. NIOSH and the Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA) still view the method in that manner officially. The other problem with PCM is that all fibers meeting method criteria are counted, not just asbestos fibers. The AHERA TEM method is the only procedure that was designed as a final clearance air sampling method. Only asbestos fibers/structures are counted in the analysis meeting method criteria for size, and those much smaller than can be determined by the PCM.
 |
| EPA's Silver Book |
Realize this is not something out of the ordinary the EPA's publication "Measuring Airborne Asbestos Following An Abatement Action" (otherwise known as the Silver Book) written in November 1985 on page 2-6 recommends the sample volume for the PCM analysis should be a minimum of 3,000 liters of air (though at the time of this publication it was describing the NIOSH P&CAM 239 PCM methodology). In addition, in March 2015 the EIA published a revision to the EPA's 1985 document "Guidance for Controlling Asbestos-Containing Materials in Buildings"(EPA 560/5-85-024, known as the Purple Book). This nationally peer-reviewed document was re-titled "Managing Asbestos in Buildings: A Guide for Owners and Managers." Chapter 5 (on page 88) says the minimum sampling volume of 3,000 liters of air for samples taken to meet the NIOSH 7400 method requirements for LOQ sampling. Mr. Dana Brown did a video regarding the LOQ issue and why NIOSH 7400 method is not the best choice for clearance, you can see it below.
This doesn't count that we have called for the AHERA TEM method to be utilized for asbestos-containing floor tiles and mastic removals based on our previous blog post "Asbestos Floor Tile Debate", published in the August 2017 issue of Healthy Indoors Magazine, which found that the NIOSH 7400 method is not able to analyze the type of fibers (Grade 7-Shorts and Floats that are known to be less than 5 microns) found in these materials because of the known small fiber sizes generated by floor tile work. Whether AHERA-based work or asbestos abatement where re-occupancy will occur, the surest way to make sure an area is ready to be given back to the public to be free of asbestos as practicable by current methods, and the fastest method for clearance would be the AHERA TEM method.
 |
| NYSDOL ICR56 Definition of an Asbestos Project |
Of course, those of you who work in New York State or New York City realize these requirements only apply to public and private K-12 schools. So they don't apply to other buildings, or do they? First, let's take the NYSDOL ICR56 Subpart 56-4, page 35 is the air sampling requirements. 56-4.6 "Test Methods" on page 36 says "the same NIOSH approved methodology for project air sampling and for analysis of the air samples shall be used at all phases of an asbestos project that require area air sampling and analysis, with the possible exception of clearance air sampling." This means that the NIOSH 7400 method must be followed for all phases except clearance (Phase IIC of the asbestos project) this allows you to use either the NIOSH 7400 method or the AHERA TEM method instead for clearance. So this means you have to follow the NIOSH 7400 method's LOQ requirements for all phases (Phase I B and Phase II A, B, & C) of the asbestos project. In addition, the NYSDOL ICR56 regulation for clearance is less than 0.01 f/cc so that changes the formula again. Let's use 0.009 f/cc for the L instead and still use 16 liters per minute, well that means the sample has to run for 267 minutes, almost 4 hours, and 30 minutes (a total volume of air of 4,278 liters).
 |
The consummate leader cultivates the moral law, and strictly adheres to method and discipline; thus it is in his power to control success. ~ Sun Tzu |
So why does everyone sample 1,200 liters of air for all samples? On April 8, 2011, the New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) Wadsworth Center issued frequently asked questions (FAQs) regarding asbestos/fibers analysis that were developed through the collaboration of the NYSDOH Environmental Laboratory Approval Program (ELAP) and the Bureau of Occupational Health and the NYSDOL. In this FAQ is FAQ#13: What is the minimum sampling volume to be collected for air sampling associated with (a) post-abatement (clearance) air monitoring and (b) post-abatement area monitoring for PCM analysis? The answer that was given was: Within the upcoming revision to NYS Industrial Code Rule 56, minimum air sample volume requirements
 |
| Buy our Asbestos Air Sampling Chart here. Read about our Asbestos Air Sampling Charts here. |
Saturday, July 09, 2022
AHERA Bulk Sampling Rules and Other Requirements that Apply to Asbestos Surveys.
EPA Clarifies Miscellaneous Materials Sampling - RePublished
OSHA 300A Posting Requirements and 2026 Penalty Updates: What Employers Need to Know
It’s time once again to focus on an important requirement from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) . Employers with 10...

-
The New York City Department of Environmental Protection (NYC DEP) has introduced proposed amendments to Chapter 1 of Title 15 of the Rules...
-
Image via Wikipedia The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) today invited public comment on a draft document titl...
-
… … … This debate regarding asbestos floor tiles started at the Professional Abatement Contractors of New York's ...